Using the API and SDK
With the AI Hub API and SDK, you can integrate AI Hub functionality into your own workflows and tooling by controlling AI Hub programmatically.
The API accepts RESTful HTTP requests made from a variety of tools or almost any programming language.
The SDK wraps API calls in Python classes and methods, providing a convenient way to interact with AI Hub programmatically.
Both the API and SDK cover the major use cases of AI Hub. However, their feature set isn’t identical.
-
The API can access most, but not all, of the same features as the graphical user interface.
-
The SDK can access all the same features as the API.
Prerequisites
Before using the API or SDK, you must complete several prerequisites.
-
You must have an AI Hub account. See Account setup to learn how to create or join an organization.
-
You must have an API token. AI Hub supports both AI Hub-managed tokens and, for Enterprise-tier organizations with OAuth providers configured, externally managed tokens. If supported by your organization, you can create your own AI Hub-managed tokens from the APIs settings page. If you don’t see the option to create a token, contact your organization admin for next steps.
-
You must have your organization ID or user ID to use in the
IB-Contextheader that’s included with every API or SDK call. Read the context identification documentation to understand how to use theIB-Contextheader, including where to find your organization or user ID.
Using the API
You can call API endpoints with any of these techniques.
-
Use the
curlcommand. -
Use code in any language that makes HTTP requests.
-
Use the AI Hub Postman collection.
-
Use the playground feature in the API reference documentation.
https protocol. Using the http protocol produces unpredictable responses.curl
The curl command line tool makes HTTP requests, including calls to API endpoints. The documentation for every AI Hub API operation includes sample code for calling the API with curl.
For example, running this command in a terminal sends a POST verb to the batches endpoint, to create a resource called a batch.
Before calling the API with curl, set these environment variables:
With the environment variables defined, the previous create batch command returns a JSON object with the ID of the new batch and no errors.
Code
Most languages can make HTTP requests. To call an API endpoint using code, submit an HTTP request with the appropriate HTTP verb and parameters.
These snippets of code send the POST verb with a { "name": "test" } JSON payload to the batches endpoint in different languages.
Go
Java
Node
Python
Before making API calls from code, set the environment variables API_ROOT, API_TOKEN, and IB_CONTEXT.
If you set these environment variables and run any of the code snippets, the API returns the ID of the newly created batch and no errors.
Postman
An AI Hub API collection is available in Postman, a platform for building and using APIs. The AI Hub collection includes automation, so responses from one API call are automatically populated in later calls.
Configure Postman
To get started, click Run in Postman and fork or import the collection. If given the option, enable notifications for any changes to the collection.
After making a copy of the collection, set up your authorization and context identification variables.
-
In Postman, in the left sidebar, click Instabase AI Hub.
-
Click the Variables tab.
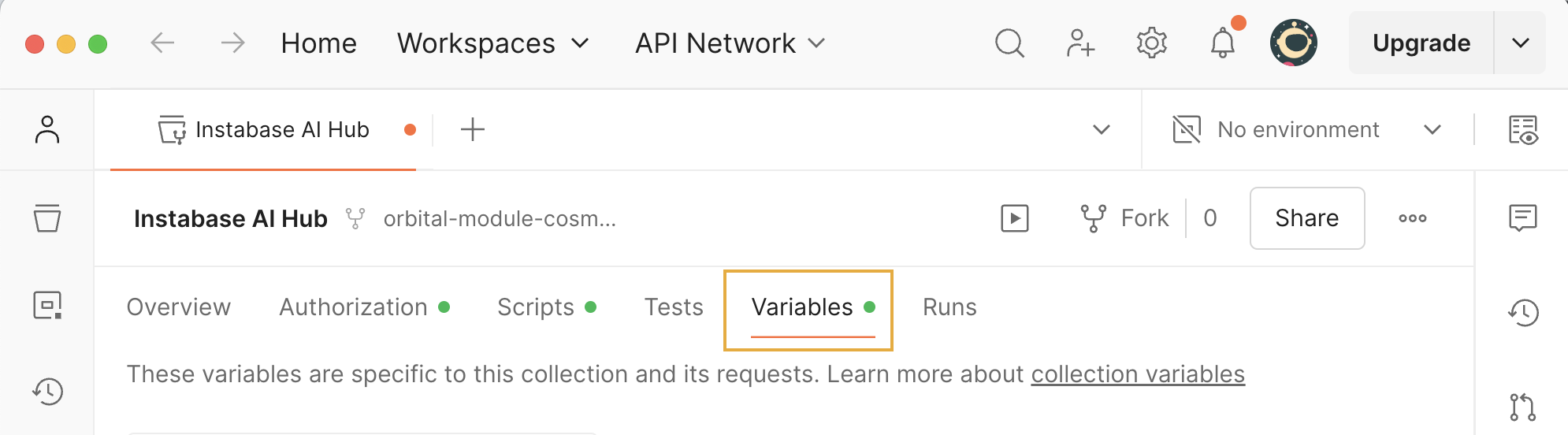
- Update the Current value column for the following variables.
- Click Save to complete Postman configuration. It’s now ready to call the AI Hub API.
To test your Postman configuration, make an API call to create a batch. Making a batch is a free operation that doesn’t use any consumption units.
-
Navigate to the App Run > Create batch endpoint.
-
Click Send.
The Body tab shows a JSON object with an id key and an integer value.
Playground
Every page in the API reference section of the AI Hub documentation includes an interactive playground that lets you build and send requests. The playground isn’t suitable for production use, but is a convenient way to learn about the API.
For example, use the navigation pane to visit the API reference > Runs > Run deployment page and click Try it in the sample code frame.
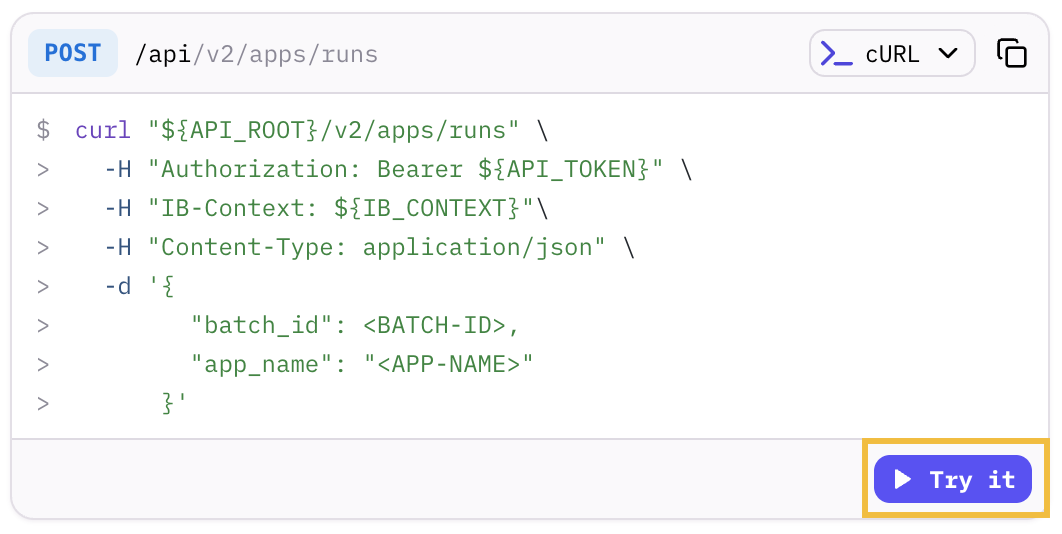
To see the playground in action, use it to make an API call to create a batch. This particular call is a free operation that doesn’t use any consumption units.
-
Navigate to the create batch endpoint documentation page.
-
In the sample code frame, click Try it to open the playground.
-
Enter an API key. Click Enter your bearer token, enter your API token, then click Close.
-
(Optional) If your organization uses a custom AI Hub domain, edit the root API URL. Double-click the request URL at the top of the playground page and edit the root URL from
https://aihub.instabase.com/apitohttps://<YOUR-DOMAIN>.instabase.com/api. -
In the Body Parameters section, enter
testas the value of thenameparameter. -
Click Send Request.
The RESPONSE box shows a JSON object with an id key and an integer value.
curl, Typescript, or Python, based on the selector in the top right. The copy icon above the sample code lets you paste sample code into your own scripts.Using the SDK
Install the SDK
The SDK is published to the Python Package Index (PyPI). This command installs the SDK if it’s not installed, upgrades the SDK if an earlier version is installed, and does nothing if the latest version is installed.
Initialize the SDK
The first step in using the SDK is initializing a client object with custom api_root, api_key, and ib_context values. The client handles authorization and context identification and provides methods for making API calls.
To initialize the SDK, start a Python script with this code.
Parameter reference
With the SDK installed and initialized, you can use any SDK sample code provided in the API or SDK documentation pages.
 SDK sample code from an API documentation page
SDK sample code from an API documentation page
Test the SDK
Confirm that the SDK is installed and initialized by adding this line under your initialization code and running the whole script.
If the output includes id=<INTEGER> and no errors, the SDK is working as expected.
Next steps
With your setup complete and tested, you’re ready to interact with the AI Hub API by making direct calls or by using the SDK.
Here are some things you can try next.
-
Run an automation app using the SDK.
-
Learn about API endpoints with the API reference documentation.
If you prefer to make API calls using the SDK, look for SDK examples in the documentation for supported endpoints. -
Learn how to track consumption unit usage for AI Hub operations.
-
Learn about service accounts, which let your organization make API or SDK calls that aren’t tied to a particular user.
-
Review AI Hub release notes, which include API and SDK changes.
